Deployment topologies¶
1. Splunk native deployment¶
There are different ways to deploy and use the Nmon for Splunk App, basically the application works in 2 modes:
- Real Time: An nmon process runs on the server and generates performance and configuration for the host, Splunk retrieves, transforms and indexes the data using the TA-nmon
- Cold Mode: The Application is being used to manage collection of nmon raw files generated out of Splunk (nmon instances have terminated and files are closed)
These deployment scenarios are detailed in the deployment section, as in an introduction, here are some deployment scenarios.
Real time deployment scenarios:
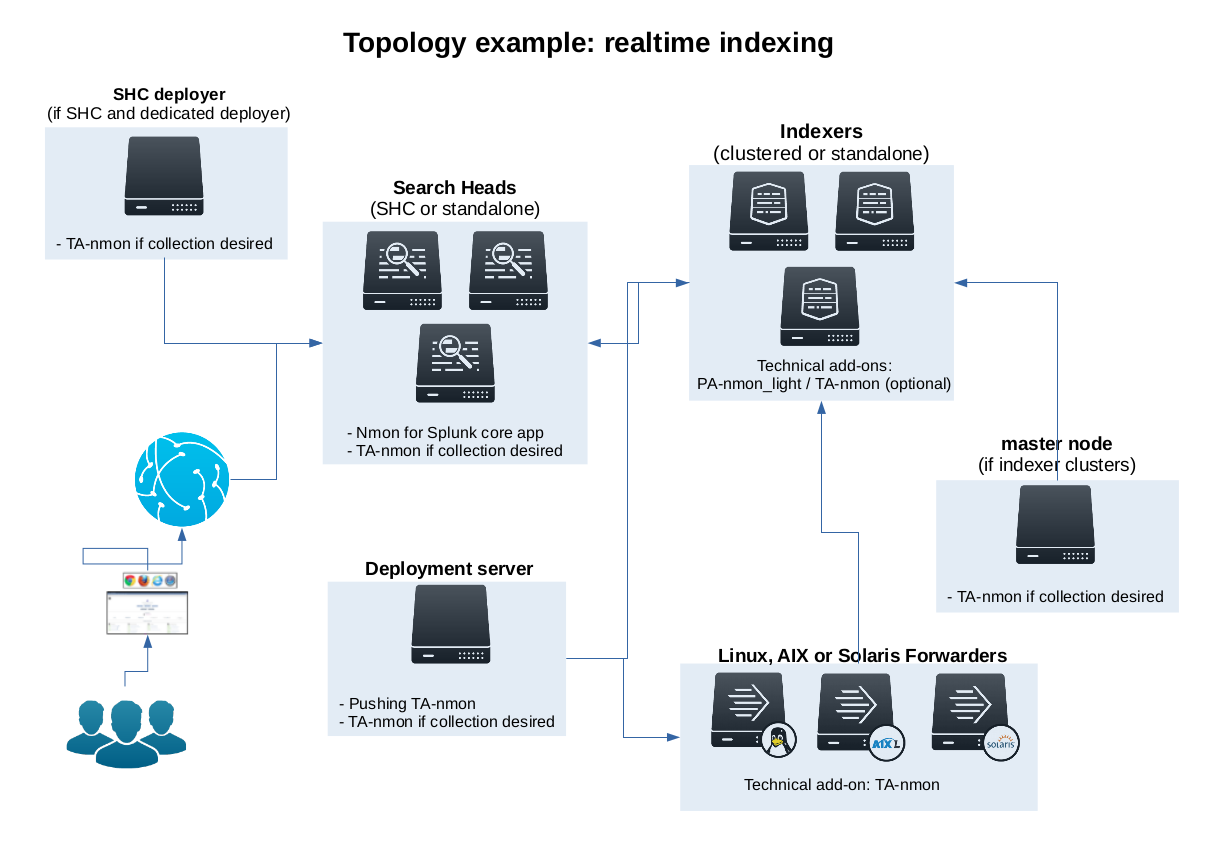
This is an example of deployment for standard scenario with multiple *nix clients running the addon “TA-nmon”, managed trough a deployment server, indexing Nmon data into a Splunk indexer cluser running the addon “PA-nmon_light” and optionally the “TA-nmon”, exploiting Nmon data in a Search Head cluster running the core “nmon” application and optionally the “TA-nmon” addon.
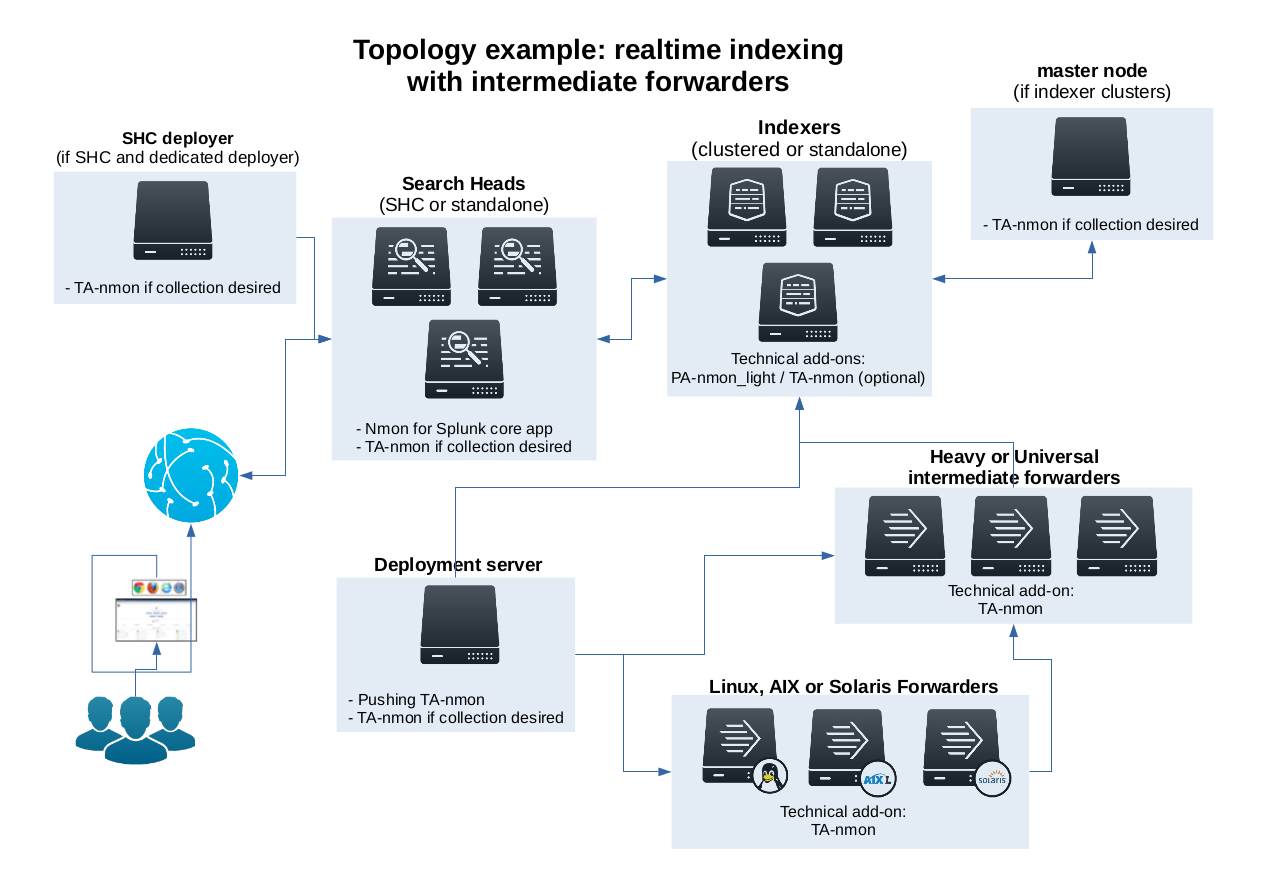
This is an example of deployment for standard scenario with multiple *nix clients running the addon “TA-nmon” and sending data to intermediate Heavy or Universal Forwarders, all managed trough a deployment server, indexing Nmon data into a Splunk indexer cluser running the addon “PA-nmon_light” and optionally the “TA-nmon”, exploiting Nmon data in a Search Head cluster running the core “nmon” application and optionally the “TA-nmon” addon.
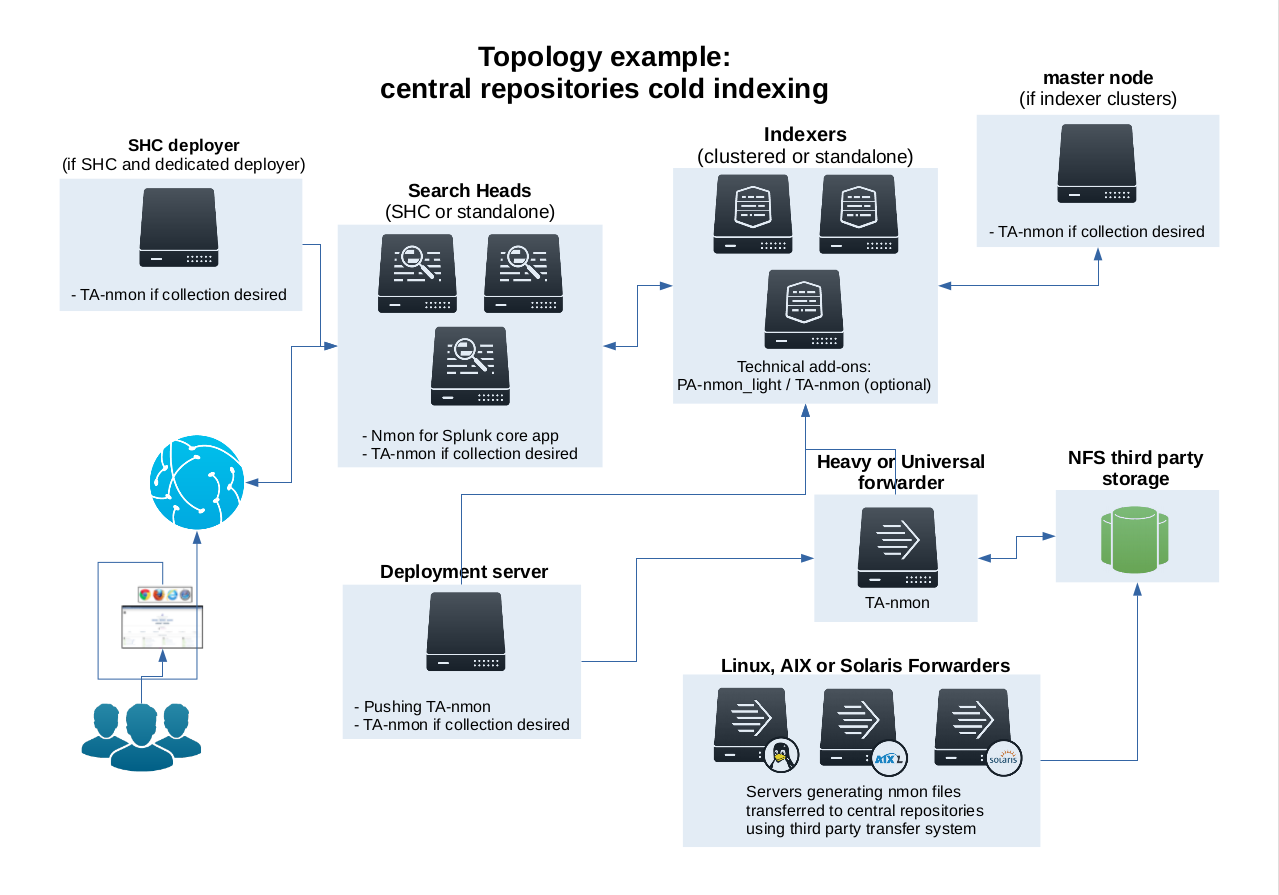
Cold data deployment scenario:
This is an example of deployment for standard scenario with a single Splunk forwarder instance (Universal or Heavy) running the addon “TA-nmon”, indexing Nmon data from central NFS repositories into a Splunk indexer cluser running the addon “PA-nmon_light” and optionally the “TA-nmon”, exploiting Nmon data in a Search Head cluster running the core “nmon” application and optionally the TA-nmon addon.
2. Agentless deployment with Splunk HEC and nmon-logger¶
Since the version 1.9.10, the nmon-logger for Splunk HEC provides a 100% agent less configuration using the Splunk http input:
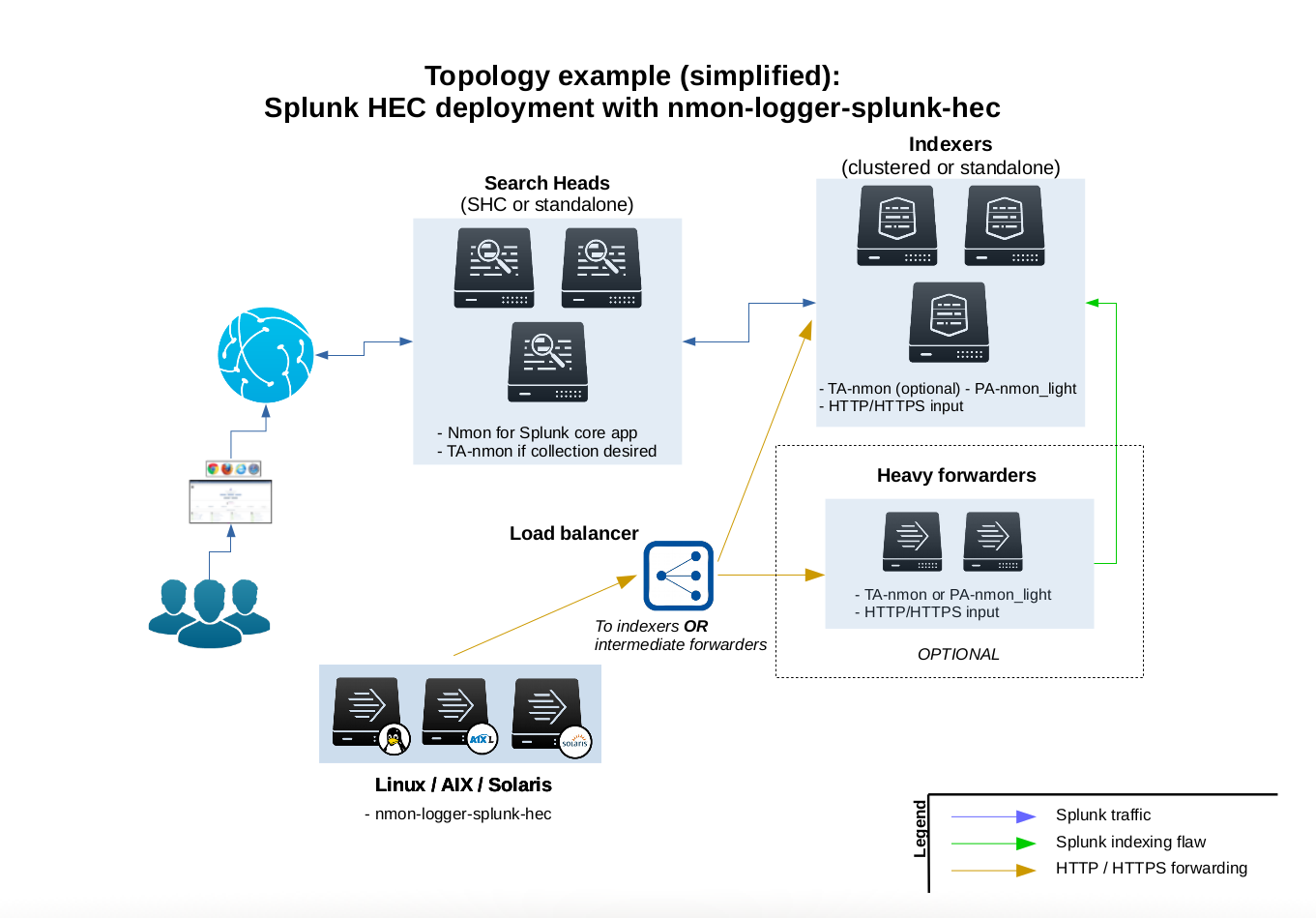
This deployment provides the following features:
- clients easy set up: the nmon-logger is provided as deb/rpm package, easy and fast deployment
- server easy set up: Splunk http input is easy to configure and implement
- 100% agent less: the nmon-logger uses only native system features (cron, logrotate…)
- secure: Splunk http traffic can easily be encrypted via SSL and integrated into any DMZ or similar restricted networking layer
- resilient and scalable: using load balancers and multiple nodes provides resiliency and horizontal scalability
- network friendly: as Web service, it can be easily used across wide networks and over the Internet
- easy management: since the http input is managed on a token basis, you can easily configure different token to ingest the data into different indexes without any package modification or complexity
See the detailed section: Splunk HEC / nmon-logger deployment
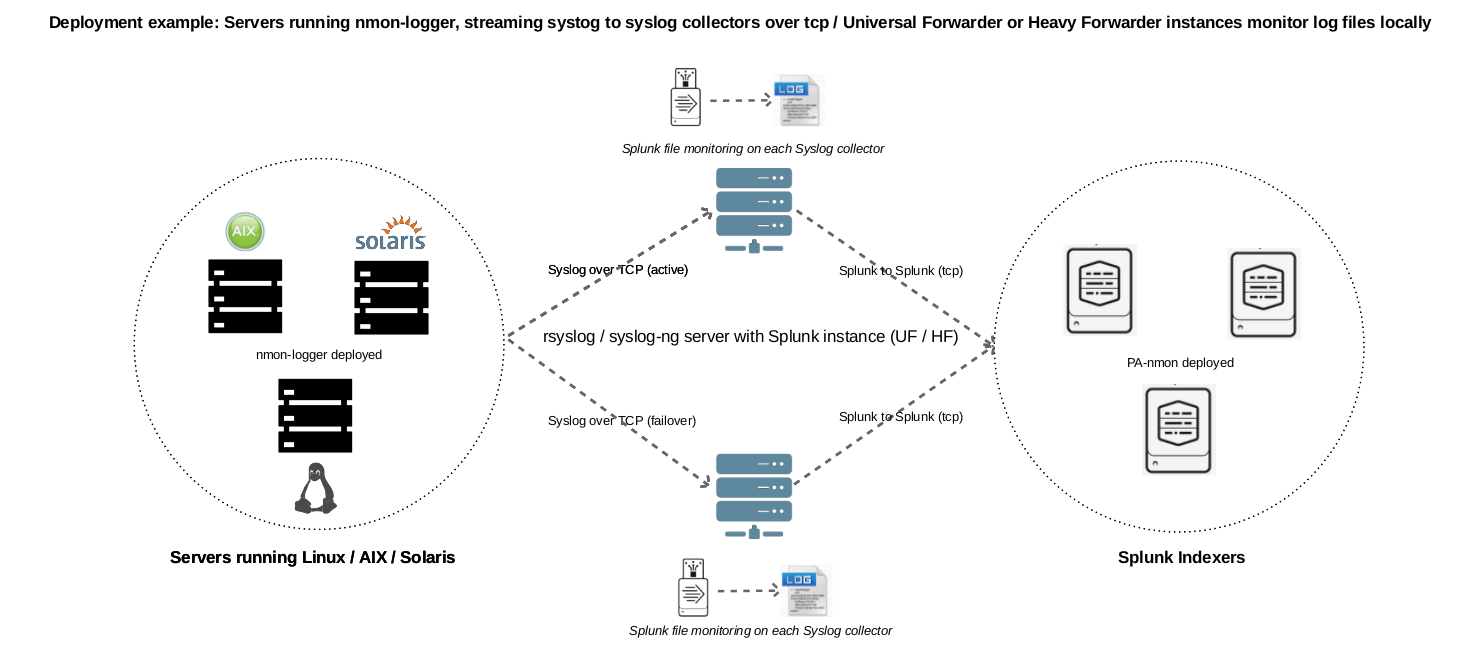
3. Syslog deployment¶
Additionally and since the version 1.6.14, it is possible to use Syslog as the transport layer associated with a third party package called “nmon-logger”
This deployment topology provides all the application features without any deployment of Universal Forwarders on end servers, using rsyslog or syslog-ng. Such a deployment answers the need for people that cannot or do not want to install any third party agent.
The nmon-logger package is available for download in GitHub: https://github.com/guilhemmarchand/nmon-logger
The deployment will use and require and/or recommended:
- nmon-logger
- rsyslog or syslog-ng
- cron
- logrotate
Note that this deployment scenario would be recommended mostly with a modern Linux deployment. Although all pieces of software should work fine too on AIX and Solaris, this requires quite up to date versions (for rsyslog / syslog-ng), which could be complex on older OS.
Example 1: Splunk Universal or Heavy forwarder installed on main syslog-ng collectors:
Example 2: Splunk Universal or Heavy forwarder installed third party servers running syslog-ng:
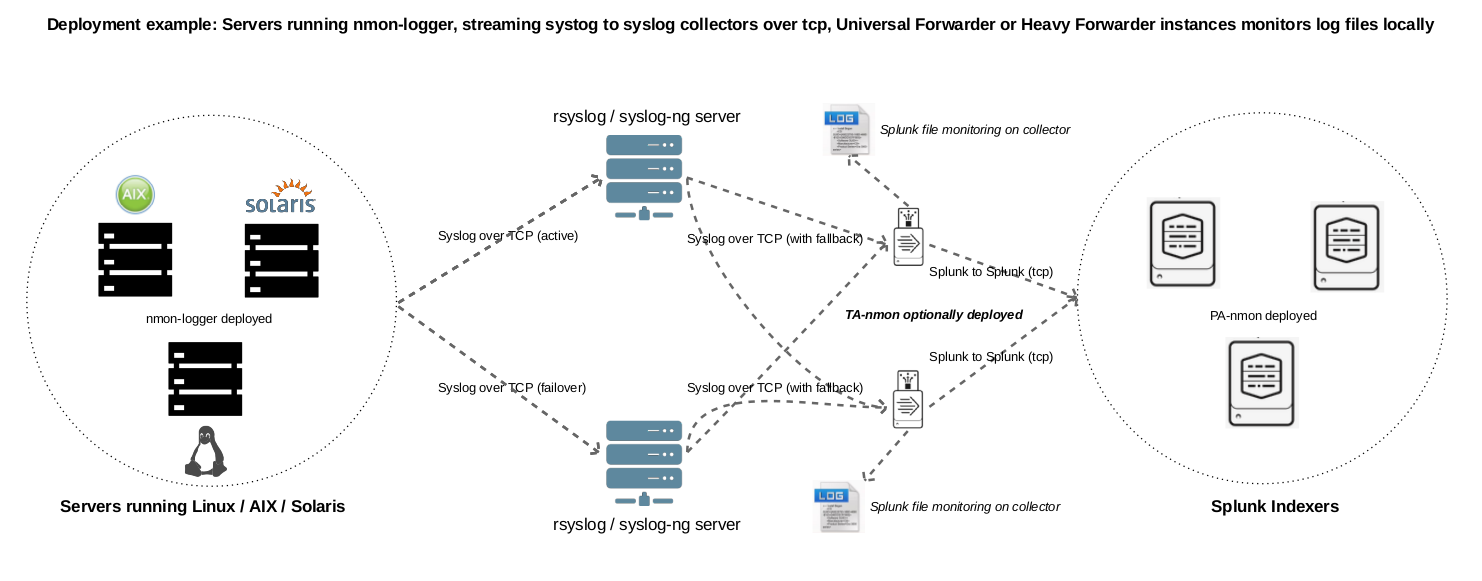
For rsyslog, see: rsyslog / nmon-logger deployment
For syslog-ng, see: syslog-ng / nmon-logger deployment